and Detail Drawings
Wales
England
- Offices
- Shops / Commercial
- Industrial Buildings
- Storage / Assembly Buildings
- Other Non-Residential
Flat Roof - Types
Introduction
- A roof is defined in BS 6229 as a flat roof if it has a pitch of 10 degrees or less.
- A flat roof must be strong, durable and stable throughout its lifetime. It must provide adequate protection against the elements, keeping the buildings structure and interior dry.
- Flat roofs have a reputation of failing early but improvements in strength, flexibility, ageing and weather resistance mean that, if built with care, using the correct materials, today’s high performance felts can have a life span of up to 20 years.
Roof Types
Flat roof constructions are generally classed as either ‘Cold’ or ‘Warm’ roofs depending on the position of the thermal insulation.
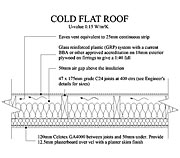
The Cold Roof

- Although not recommended today, and actually banned in Scotland, until recently cold flat roofs were fairly common.
- In a cold roof the thermal insulation is laid between the joists below the structural deck.
- As the insulation is not required to take any loads, quilts and other loose fill materials can be used as well as rigid insulation.
Add To Basket
Includes DXF,
DWG & JPG
- Because the structural elements of a cold roof are not protected by from the heat of the sun by a layer of insulation they are liable to suffer the damaging effects of thermal movement.
- Ventilation is required above the insulation in a cold roof to prevent the build up of moisture vapour in the roof void.
This is just a Small Sample from our Drawing Library.
Warm Deck Roof
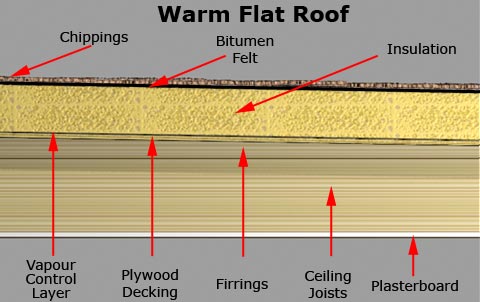
- In a warm deck roof the insulation is positioned above the structural deck and no ventilation is required.
- Throughout the course of the year the roof deck and all below it is kept at a temperature close to that of the inside of the building, therefore the roof structure is protected from extremes of hot and cold, lessening the potential for damage caused by thermal movement.

Add To Basket
Includes DXF,
DWG & JPG
- A warm deck also provides added protection from the dangers of condensation as the structure is kept warm, at a temperature above dewpoint, by the insulation above it. Therefore water vapour which enters the roof structure from the room below will not have a cold surface on which to condense. NHBC recommend that this type of roof be considered as the standard form of construction.
Types of Warm deck roof
There are two forms of warm deck roof:
- Sandwich
- Inverted
Warm Deck: Sandwich Roof
- The sandwich warm deck roof is the most common type of flat roof. The insulation is placed below the waterproof covering and is either mechanically fixed or bitumen bonded on to the top of the deck.
Inverted warm deck roof
- The insulation boards in an inverted warm deck are laid over the structural deck and the waterproof covering. The insulation is secured by a layer of ballast or paving slabs to prevent wind uplift.
- The waterproofing membrane has the added protection of the insulation from foot traffic and degradation caused by exposure to solar radiation. However, it may be a more difficult to locate defects in the membrane.
- Proprietary systems are available now which combine the insulation and ballast layers.
Flat Roof - Types
Introduction
- A roof is defined in BS 6229 as a flat roof if it has a pitch of 10 degrees or less.
- A flat roof must be strong, durable and stable throughout its lifetime. It must provide adequate protection against the elements, keeping the buildings structure and interior dry.
- Flat roofs have a reputation of failing early but improvements in strength, flexibility, ageing and weather resistance mean that, if built with care, using the correct materials, today’s high performance felts can have a life span of up to 20 years.
Roof Types
Flat roof constructions are generally classed as either ‘Cold’ or ‘Warm’ roofs depending on the position of the thermal insulation.
The Cold Roof

- Although not recommended today, and actually banned in Scotland, until recently cold flat roofs were fairly common.
- In a cold roof the thermal insulation is laid between the joists below the structural deck.
- As the insulation is not required to take any loads, quilts and other loose fill materials can be used as well as rigid insulation.

Add To Basket
Includes
DWG and Jpeg
- Because the structural elements of a cold roof are not protected by from the heat of the sun by a layer of insulation they are liable to suffer the damaging effects of thermal movement.
- Ventilation is required above the insulation in a cold roof to prevent the build up of moisture vapour in the roof void.
Warm Deck Roof

- In a warm deck roof the insulation is positioned above the structural deck and no ventilation is required.
- Throughout the course of the year the roof deck and all below it is kept at a temperature close to that of the inside of the building, therefore the roof structure is protected from extremes of hot and cold, lessening the potential for damage caused by thermal movement.

Add To Basket
Includes
DWG and Jpeg
- A warm deck also provides added protection from the dangers of condensation as the structure is kept warm, at a temperature above dewpoint, by the insulation above it. Therefore water vapour which enters the roof structure from the room below will not have a cold surface on which to condense. NHBC recommend that this type of roof be considered as the standard form of construction.
Types of Warm deck roof
There are two forms of warm deck roof:
- Sandwich
- Inverted
Warm Deck: Sandwich Roof
- The sandwich warm deck roof is the most common type of flat roof. The insulation is placed below the waterproof covering and is either mechanically fixed or bitumen bonded on to the top of the deck.
Inverted warm deck roof
- The insulation boards in an inverted warm deck are laid over the structural deck and the waterproof covering. The insulation is secured by a layer of ballast or paving slabs to prevent wind uplift.
- The waterproofing membrane has the added protection of the insulation from foot traffic and degradation caused by exposure to solar radiation. However, it may be a more difficult to locate defects in the membrane.
- Proprietary systems are available now which combine the insulation and ballast layers.
To begin compiling your Building Regulations Specification with one of our Web-Apps, choose either House Extension, New Build, Flat Conversion, Loft Conversion, Garage Conversion, Basement Conversion, Flat Conversion, New Build Flats or Garage Build.














